Beta…hydro…what? Technical and “science-y” words can be super intimidating, but we’re here to break down one of the top buzz words in the ketogenic diet community — betahydroxybutryate (or BHB). We’ll chat all about what BHB is, why you’d want to use it for energy, and all about side effects and benefits of BHB.
WHO CARES?
Are you ready for a very basic metabolism overview? Most modern humans break down carbohydrates into glucose and this then breaks down further and enters mitochondria to produce ATP, which is the energy system of your cells. In other words, you use carbs for energy. When you are on a ketogenic diet, you are breaking down fats into things called ketone bodies, and this is how you provide your body with energy, instead of via carbohydrates. So, you’re either using carbohydrates for fuel or fat for fuel.
Why is this desirable? Think about energy production in your body much like macro energy consumption on a planetary level. Coal is gross and dirty and messes tons of different things up. You need to continue to burn it to get energy. Solar power is free, clean and pretty much limitless. This is pretty much the same story when you are burning carbs (coal) versus fats (solar) for energy.
WHAT IS BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE OR BHB?
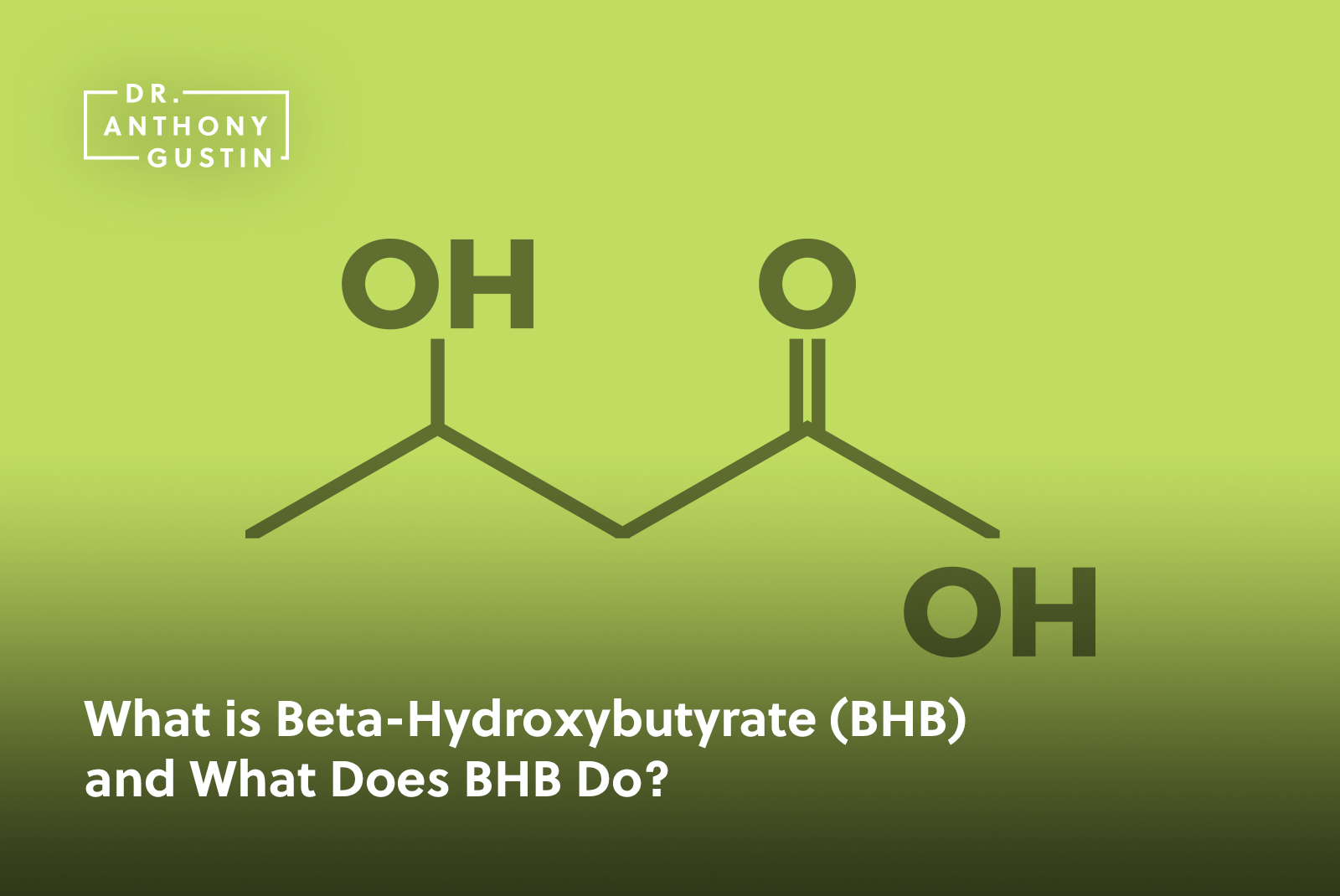
Beta hydroxybutyrate, or simply BHB, is a molecule that is considered a “ketone body.” It is one of the main molecules that helps your body produce energy in the absence of glucose.
This molecule is quite essential if you are using your own fat for fuel, or taking BHB as an exogenous ketone supplement to increase energy production — essentially to be in nutritional ketosis. If you’re not certain about what ketones are or what nutritional ketosis is, you should back up a little bit and read more about that on my company site, Perfect Keto.
Geek note: Technically speaking, beta hydroxybutyrate is NOT a legitimate ketone body. Ketone bodies, or ketones are technically molecules with carbonyl carbons which are bonded to two additional carbon atoms. One carbon has four available bonds. When that carbon is double bonded to oxygen and also has two single bonds to carbon, we have a ketone body. If you have a carbon atom that is double bonded to an oxygen (carbonyl group), which is also bound to an -OH group instead of two different carbon atoms, that would be a carboxylic acid, but that really doesn’t matter in this case. For all intents and purposes of the ketogenic diet, betahydroxybutyrate should be considered one of the three ketone bodies and a “ketone” nonetheless. Your body uses BHB pimarily for energy in the state of ketosis, so it’s a ketone, okay?
Tip: Beta hydroxybutryate, or BHB, is not GHB.
BHB and GHB sure sound a lot alike, but don’t get these confused! One is ketone body and one is a party drug. Not the same.
WHERE DOES BHB COME FROM?
ENDOGENOUS BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE (YOUR BODY MAKES IT)
Beta hydroxybutyrate can be made in the body. Endogenous means your body makes it. Think EN = in.
When your body is done using up a certain substrate to create energy (acetyl-CoA) after eating carbohydrates, it will start to find creative ways to get the job done. This is something that you want to happen. This is the switch to ketosis. If you didn’t do this, you’d be dead after fasting for a very short period of time. Under normal circumstances, the liver will start making beta-hydroxybutyrate from long chain and medium chain fatty acids that are liberated from your fat tissue. You are turning fat into fuel. Good work. This is why people can fast for months at a time and still function like normal humans.
You can also get beta-hydroxybutyrate and other ketones through your diet.
EXOGENOUS BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE (YOU PUT IT INTO YOUR BODY)
Sometimes waiting for your body to make the switch from carbohydrate metabolism to beta hydroxybutyrate metabolism (aka ketosis) can be an uncomfortable and lengthy process. Another way to get beta hydroxybutyrate into your system so your body is using “clean” energy is by taking it supplementally or through nutrition. A betahydroxybutyrate supplement is what can be used in this scenario. This is an exogenous ketone. Exogenous means you get it from outside of your body. Think EX = exit = outside.
The way you make an exogenous BHB is by attaching it to some type of other compound (sodium, potassium, calcium, or magnesium) so that your body can process the molecule by cleaving the bond between the salt and the beta hydroxybutyrate. BHB + bound to a salt = BHB salts, which is what most people in the ketosis community call exogenous ketones. There are also things called esters, which are basically unbound BHB molecules. These are really disgusting and cause massive digestive issues, so I like to ignore them until we can produce them in a more appealing way.
Ok, so beta hydroxybutyrate is a compound that your body makes from fat in the absence of carbohydrate intake, or that you can take supplementally, but what does it really do and why should you care?
If all you care is that it provides you with energy, excellent. You can skip to the end of this article. If you’re curious about how this happens, please continue.
WHAT DOES BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE DO?
As we learned earlier, beta hydroxybutyrate is the first substrate that kicks the metabolic state of ketosis into action. Revisiting the scenario from before, if you either take supplemental forms or if your body is making beta hydroxybutyrate, BHB is able to be processed in your body with the result being lots of clean energy.
Beta hydroxybutyrate floats around in your blood, and importantly, can cross different barriers to be able to be turned into energy at all times. One of the most important areas where this happens is in the brain. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is usually a very tightly regulated interface that doesn’t allow the transfer of many molecules, but since BHB is such a rock star and so hydrophilic, your brain knows to let it in so it can bring energy to the party at any time. This is one of the main reasons why increased levels of ketosis lead to improved mental clarity, focus and reduction in neurodegenerative diseases.
How BHB turns into energy is a fairly simple process. As we’ve mentioned, beta hydroxybutryate eventually leads to energy production after you consume it or after your body breaks stored body fat down. It does this by going into the cell, entering the mitochondria (energy factories) at which stage it cleaves the carboxyl acid group and becomes acetoacetate (another “ketone body”). Acetoacetate turns into acetoacetyl-CoA, which then is cleaved to acetone (another “ketone body”) and acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is the whole reason we want BHB in the first place. This jumps into what is called the Kreb’s cycle (don’t you remember any of your biochemistry classes?) and is churned into ATP — the energy currency of your cells!
There you have it. BHB is important because it can freely float throughout your body in your blood, crossing many tissues where other molecules can’t, then it is processed into energy. BHB = ATP = energy.
HOW TO CHECK YOUR BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE LEVELS
Now for the one person who is still reading this after the ridiculously dry biochemistry discussion, you know all about what BHB is and what it does, you may want to know what is going on with your BHB and how much your body is using. Easy!
Since beta hydroxybutyrate is transported throughout the body via the blood, the best way to check your true BHB levels is through a blood test. The good news is that you can just use a simple finger prick and an at home method that is very similar to how diabetics check their glucose. The bad news is that it can be pretty expensive. Each strip and time you test can be around $4-6.
To be in nutritional ketosis, you’re going to want to see your levels of beta hyroxybutyrate at about 0.5 – 3.0 mmol as a reading from your blood test.
If you’re interested more in how to check your ketone levels (and betahydroxybutyrate levels) then check out the guide I wrote on how to test your ketone levels.
IS BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE SAFE?
Yes. Both producing BHB in your liver as well as supplementing with beta hydroxybutyrate very safe. As we mentioned before, levels of 0.5 – 3.0 mmol measured in a blood test are completely normal. Some people get stressed out when they hear the term “diabetic ketoacidosis” or DKA, which is an entirely different metabolic scenario where your BHB levels skyrocket to 15-25 mmol blood readings.
Diabetic ketoacidosis will not happen to you if you have a normal pancreas and essentially, aren’t diabetic. If you produce any insulin at all, you shouldn’t have a problem with this. Hint: you do.
I wrote another article on the differences between ketosis and ketoacidosis if you’re interested.
SIDE EFFECTS OF BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE
Some general side effects of your body producing beta hydroxybutyrate is essentially the lull in time it takes to switch from carbohydrate metabolism to fat metabolism, which can take 3-4 days. This can lead to mood swings, fatigue, and general low energy. If you want to skip that step, we recommend taking exogenous BHBs to switch your body over effortlessly.
Some of the side effects of taking too much supplemental BHB is slight gastrointestinal distress. Basically, your body isn’t used to processing all of these ketones. If this is a problem, just stair step the amount you take until tolerance. For example, 1/4 scoop for a few days, 1/2 scoop for a few days, then 3/4, then a full scoop.
It can also sometimes help if you use Perfect Keto or other exogenous ketone supplements paired with other fats, which can slow down the absorption slightly. You can also add some MCT oil powder if you want to do this.
BENEFITS OF BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE SUPPLEMENTATION
Taking exogenous ketones by way of betahydroxybutryate supplementation will rapidly get you into ketosis and force your body to start using a sustained energy source of fat breakdown. This essentially skips the whole “carb flu” and few day period where you have to restrict carbohydrates
WHEN TO TAKE BETA HYDROXYBUTYRATE
Being in ketosis all of the time is great and all, but there are some other times where you want to load your body up with some ketone bodies like betahydroxybutyrate. Some of the times when you would take a supplemental or exogenous ketone supplement would be:
– Before a workout for performance enhancement
– Daily for enhanced levels of ketosis and overall health benefits
– After a carbohydrate laden meal to get back into ketosis
– In the morning for a mental boost
– On an empty stomach to suppress hunger
I think that should probably cover anything anyone would want to know about betahydroxybutyrate. If you have any other questions leave them in the comments below!